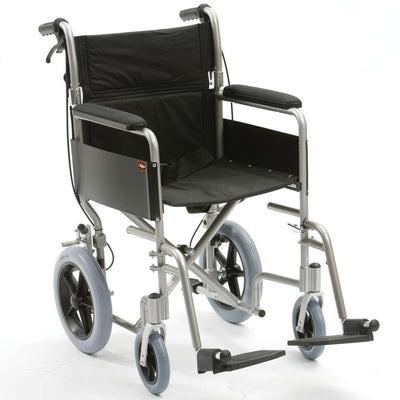
Wheelchairs are an important mobility device used by people with various conditions that limit their ability to walk or move independently. While some individuals may only require a wheelchair temporarily, others may need it on a permanent basis. The reasons people use a wheelchair are diverse, ranging from injuries, diseases, or congenital disabilities.
Injuries
This type of injury often results in paralysis or loss of sensation below the injury site, making it impossible for the affected individual to walk or move around without assistance. Other conditions that may lead to the use of a wheelchair include stroke, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and arthritis.
Injuries, such as traumatic brain injuries or amputations, can also lead to using a wheelchair. Individuals with amputations often require a wheelchair temporarily as they adapt to their prosthetic limb. A wheelchair provides the necessary support and mobility during this period of adjustment. Traumatic brain injuries can result in a loss of coordination or balance, making it difficult to walk or move around independently. A wheelchair provides stability and safety for the individual.
Health Conditions
Individuals with cerebral palsy often experience muscle stiffness or spasticity, making it difficult to walk or move around without assistance. In such cases, a wheelchair provides the necessary support and mobility for the individual. Similarly, muscular dystrophy is a genetic condition that weakens the muscles over time, leading to the loss of mobility. A wheelchair may be needed to compensate for the weakness and enable the individual to move around independently.
Arthritis is another condition that may require the use of a wheelchair. This condition is characterized by inflammation and damage to the joints, leading to pain and stiffness. Individuals with severe arthritis may find it challenging to walk or stand for extended periods, and a wheelchair provides relief and mobility.
Age-related conditions
Furthermore, age-related conditions such as Parkinson's disease, dementia, and Alzheimer's disease can also lead to mobility challenges that may require the use of a wheelchair. Parkinson's disease, for instance, affects the nervous system, leading to tremors and muscle stiffness that can impact mobility. Similarly, dementia and Alzheimer's disease can cause confusion and disorientation, leading to safety concerns while walking or moving around independently.
The reasons people use a wheelchair are diverse and complex. They range from congenital disabilities to age-related conditions and injuries. The associated conditions that require people to use a wheelchair include spinal cord injuries, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, arthritis, traumatic brain injuries, and age-related conditions. Regardless of the cause, a wheelchair is an essential tool that provides individuals with the necessary support and mobility to lead a fulfilling and independent life.